
As emerging technologies continue to advance, the food industry is undergoing disruptive transformations. One of the most notable examples is cultured meat, which has garnered global attention for its innovative and environmentally sustainable features.
Cultured meat, a meat alternative produced through technological means, essentially represents a more controlled industrial production process. It replaces traditional meat production steps such as farming, slaughtering, and transportation. This ensures that cultured meat is free from environmental contamination and animal-borne diseases while maintaining safety and nutrition. Consequently, it enables more stable and efficient production.
Key Drivers Behind the Growth of the Cultured Meat Industry
The development of the cultured meat industry not only enriches consumer food choices but also offers new solutions for global food security challenges and environmental sustainability.
1.Traditional livestock farming exerts significant pressure on the environment.
Livestock emit greenhouse gases such as methane, contributing to global warming. Additionally, raising large numbers of animals requires vast land areas for grazing and feed cultivation, as well as extensive water resources. Cultured meat addresses these issues by reducing pollution and resource waste.
2.Meeting Health Demands
Cultured meat, particularly plant-based meat, has the advantage of being low in cholesterol. The production process allows for precise control of added fats, salts, and other components while incorporating nutrients like vitamins and minerals, aligning with modern dietary health trends.
3.Enhancing Animal Welfare
Traditional meat production involves animal farming and slaughter. Large-scale adoption of cultured meat could reduce harm to animals, contributing to better animal welfare.
4.Easing Resource Strain
Population growth has led to increasing meat demand, which traditional livestock farming may struggle to meet. Cultured meat offers a supplementary method to ensure meat supply, alleviating resource pressure.
Categories of Cultured Meat
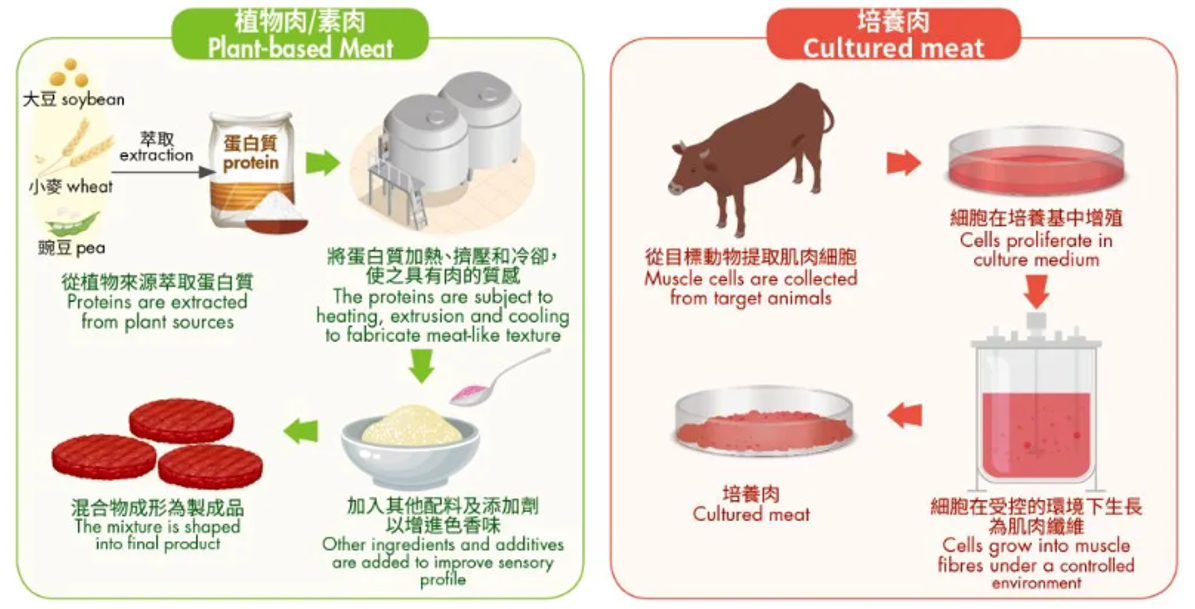
Plant-based meat is derived mainly from plant proteins, such as soy protein, pea protein, rice protein, and wheat protein. Through processing techniques like extrusion, heating, and cooling, plant proteins are transformed into products with textures and tastes resembling animal meat. Common examples include plant-based burgers and sausages.
Cell-cultured meat is cultivated using animal stem cells (or, in some cases, other types of cells such as muscle or fat cells). The process begins by extracting cells from animals and placing them in a culture medium enriched with nutrients (e.g., glucose, amino acids, vitamins, and inorganic salts), growth factors, and other essential components. Under controlled conditions of temperature, humidity, and gas composition, the cells proliferate and differentiate into muscle tissue inside specialized containers such as bioreactors. The result is cultured meat that closely resembles real meat in cellular composition and structure.
The first "lab-grown burger," developed from cow stem cells, was introduced in 2013 by the Netherlands-based Post Laboratory under the leadership of Professor Mark Post. Although the initial cost was prohibitively high, this breakthrough laid the foundation for subsequent research.Since then, numerous research teams and companies worldwide have been investing in the development of cell-cultured meat, accelerating advancements in the technology.
Several countries have begun approving the production and sale of cell-cultured meat, paving the way for global market expansion.The United States and Singapore, for example, have authorized specific cell-cultured meat products to enter the market. These developments are expected to encourage other countries to establish regulatory frameworks and open their markets.The cell-cultured meat sector has also attracted significant investment. Funding from venture capital firms, along with involvement from traditional food companies and tech enterprises, has spurred research and industrialization efforts in this field.
Despite rapid advancements and promising applications, the development of cell-cultured meat faces several hurdles:
1.High Costs
The production of cell-cultured meat is complex and relies on expensive culture medium components, such as fetal bovine serum. This makes it challenging for cultured meat to compete with traditional meat in terms of price. Companies are actively researching animal-free culture media to lower costs and improve sustainability.
2.Technological Bottlenecks
At present, cell-cultured meat is still in the laboratory or small-scale production stage. From both economic and environmental perspectives, large-scale production processes are needed to improve efficiency and ensure sustainability in the production process.To achieve large-scale industrial production, significant technological breakthroughs are required in areas such as bioreactor design and optimization of cell culture conditions. For example, the development of larger bioreactors capable of precisely controlling parameters is critical to meet market demands.Additionally, the formation of muscle and fat tissues in cell-cultured meat differs from traditional livestock meat, making it a major challenge to replicate the fiber structure and texture of natural meat.
3.Regulatory Systems
As a novel food, the lack of comprehensive legal and regulatory frameworks is a significant obstacle to the growth of the cultured meat industry. Establishing a complete standard system is essential to build consumer confidence in cultured meat products.International food safety organizations are actively working to develop relevant standards to ensure the safety and trustworthiness of cell-cultured meat.
4.Consumer Acceptance
Consumer awareness and acceptance of cell-cultured meat remain limited, as doubts persist about this unconventional method of meat production.Education and marketing are crucial to increasing consumer understanding and acceptance of cell-cultured meat. Many companies and organizations are striving to improve public perception through transparent information and proactive market promotion.
Morimatsu’s Solutions for the Cultured Meat Sector
With the rapid growth of the cell-cultured meat industry and the increasing maturity of large-scale cultivation technology, more companies are seeking solutions for expansion and large-scale production. Morimatsu has accumulated extensive experience in the food industry and offers a wide range of core equipment and services for clients in the cultured meat sector. These include bioreactors, liquid preparation systems, storage systems, feeding systems, HTST sterilization systems, CIP systems, and cell separation tanks. The key advantages include:
· Advanced Scaling Design Principles: Featuring multiple aeration systems, stirring systems, and stable temperature control mechanisms, along with precise feeding methods and integrated online monitoring electrodes. These systems are capable of ensuring stable production of various cultured animal cells.
· Customizable Automated Cleaning Systems: Designed to guarantee effective cleaning while emphasizing energy efficiency and reducing consumption.
· Rationalized Zoning Layout Design: Functional areas such as main process units, filtration stations, feeding units, temperature control units, and waste disposal units are designed independently to ensure operational autonomy and avoid interference. The design also prioritizes ease of operation and maintenance while balancing aesthetic appeal and simplicity, providing clients with an exceptional user experience.
Cultured meat represents a transformative opportunity for the future of the food industry. Morimatsu actively explores and invests in this emerging field, accelerating the technological evolution and industrialization of cultured meat. By doing so, the company contributes to the development of a sustainable, eco-friendly, and innovative food industry, shaping a greener and more sustainable future.
About Morimatsu LifeSciences
Morimatsu LifeSciences, one of the key business segments of Morimatsu International Holding Co., Ltd. (Morimatsu International, stock code: 2155.HK), mainly consists of Shanghai Morimatsu Pharmaceutical Equipment Engineering Co., Ltd., Morimatsu (Suzhou) Life Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Morimatsu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Pharmadule Morimatsu AB (Sweden) and its subsidiaries, which serves the pharmaceuticals, bio-pharmaceutical, cosmetic medicine, FMCG (cosmetics, baby, women & home Care, health care, fabric & home care, food, beverage, nutraceuticals) and other industries, providing customers with "core equipment+value-added services+digital intelligent overall factory solutions and services" ("MVP Solutions&Services"), focusing on core equipment, stainless steel process systems, disposable process systems, consumables, laboratory solutions, digital and modular factory solutions and services.
As a diversified multinational company, Morimatsu has opened subsidiaries or advanced manufacture plants in China, Japan, Sweden, United States, India, Italy, Singapore, and has delivered different forms of products and services to more than 40 countries and regions so far, by its global footprint of an efficient and professional team.
Forward-Looking Statements
The information in this press release may include some forward-looking statements. Such statements are essentially susceptible to considerable risks and uncertainties. The use of "predicted", "believed", "forecast", "planned" and/or other similar words/phrases in all statements related to our company is to indicate that the statements are forward-looking ones. Our Company undertakes no obligation to constantly revise such predicted statements.
Forward-looking statements are based on our Company management's current perspectives, assumptions, expectations, estimations, predictions and understanding of future affairs at the time of the making of such statements. Such statements are not guarantees of future development and are susceptible to the impact of risks, uncertainties and other factors; some are beyond the control of our Company and unpredictable. Subject to the influence of future changes and development in our business, competition environment, political, economic, legal and social conditions, the actual outcomes may differ significantly from the information contained in the forward-looking statements.