
Microfluidic Technology is an interdisciplinary technology that has recently achieved notable progress in fields such as biomedicine, cosmetics, and biopesticides. It shows significant potential for application, with the promise of driving the development and upgrading of related industries.
What is Microfluidic Preparation Technology?
Microfluidic preparation technology, based on microfluidic chip channels, precisely controls the flow rate, volume ratio, mixing sequence, and position of raw materials. This technology enables the design of diverse monodisperse droplet structures that can encapsulate active ingredients. Due to its precise control over minute fluid volumes, microfluidic preparation technology allows for the design of various microemulsions and monodisperse delivery vehicles encapsulating active ingredients, thereby endowing the active components with features such as stability, sustained release, and targeting.
Microfluidic Chip Structure Types: The fundamental structures of microfluidic chips include coaxial focusing, flow focusing, T-junction, and Y-junction, which can be used to prepare single droplets. By combining and improving these basic structures, it is possible to create double, multiple, or even multi-chamber droplets, achieving the efficient delivery of one or more active ingredients in a single process.
M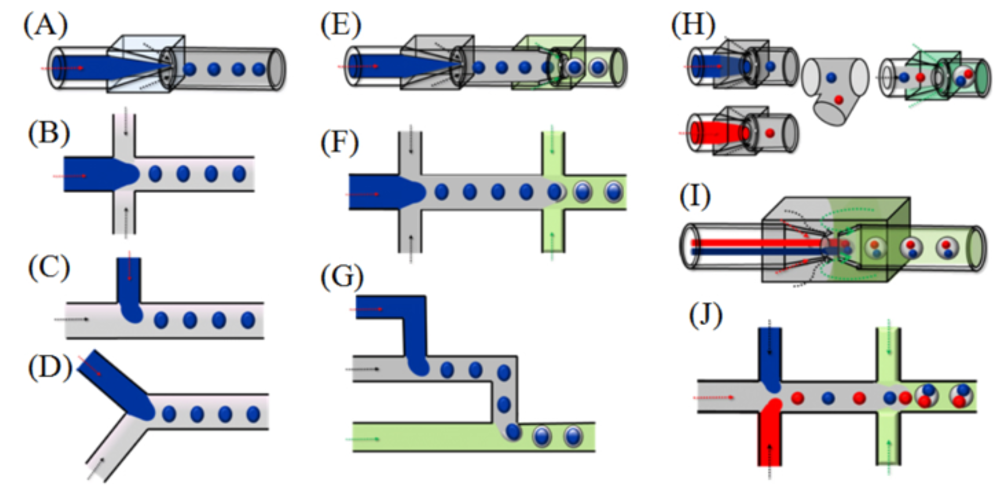
(A) Coaxial focusing device; (B) Flow focusing type; (C) T-type; (D) Y-type; (E-G) Combined type; (H-J) Improved type
Advantages of Microfluidic Preparation Technology
· High-efficiency mixing and precise control
· Enables droplet structure design, yielding uniform particle sizes
· Continuous production process, offering strong feasibility for industrial applications
Applications of Microfluidic Preparation Technology in Biomedicine
Liposomes
Targeted tumor drug delivery carriers
Liposomes are spherical vesicles with a bilayer structure, formed when phospholipids are dispersed in water. Their size ranges from several nanometers to hundreds of micrometers, and they encapsulate a water phase. As a drug carrier, liposomes can protect drugs, enhance efficacy, reduce toxicity to the body, and improve drug targeting. Doxil, the first FDA-approved nanodrug (launched in 1995), significantly reduces the cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin without compromising its antitumor activity.
Development of Functionalized Liposomes
Liposomes prepared via traditional methods often exhibit poor batch-to-batch reproducibility and considerable variation in particle size and properties, limiting many research projects to the lab stage. Microfluidic technology enables liposomes with consistent batch-to-batch quality, controllable particle size and properties, and the ability to carry multiple drugs, particularly advantageous for targeted tumor drug delivery.
The core of microfluidic technology is converging two-phase fluids to form nanoscale particles. By incorporating different drugs into the two phases, dual-drug loading is achievable; adding functionalized phospholipids or ligands attached to phospholipids in the organic phase may allow for the one-step production of multifunctional liposomes.
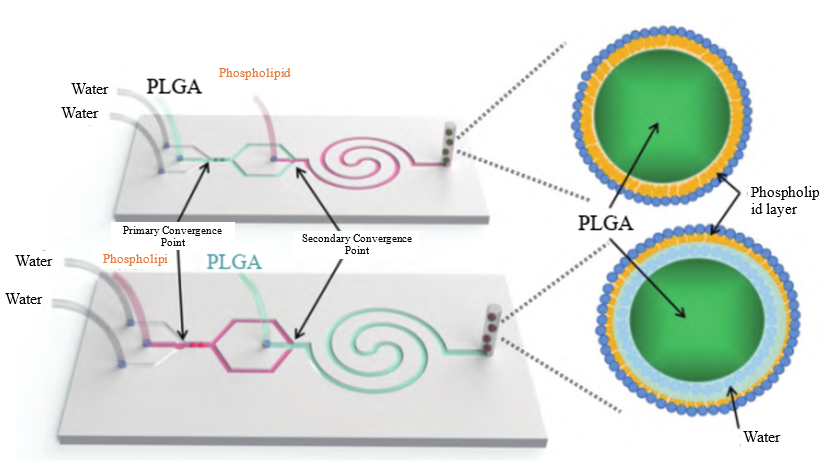
Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP)
FDA-approved Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery System
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technology is the basis for most authorized mRNA COVID-19 vaccines (including full and emergency use authorizations). Currently, over 90% of clinical mRNA drugs in development also rely on LNP delivery systems.
· siRNA Therapy: Onpattro (patisiran) is the first approved siRNA therapy, used for treating hATTR amyloidosis. LNP siRNA technology also offers new avenues for treating other genetic and chronic diseases.
· mRNA Vaccine: The successful development of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines highlights the significant potential of LNP technology in the vaccine field. LNP mRNA vaccines can effectively stimulate immune responses, contributing to epidemic control.
· mRNA Therapy: LNP mRNA systems can be used to treat various diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, liver fibrosis, and rare diseases, as well as enabling gene editing.
LNP Carrier Preparation Solution:
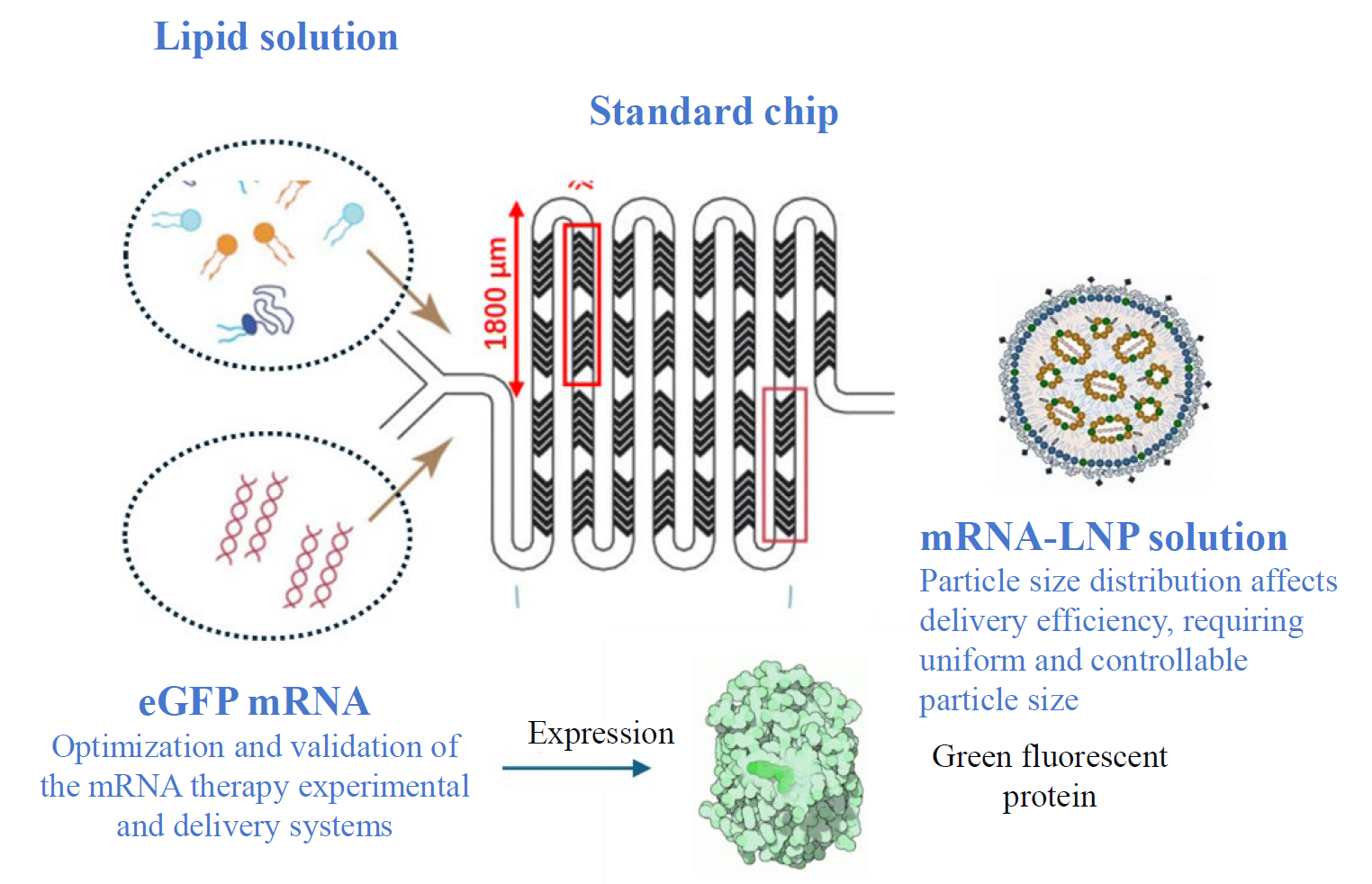
To ensure delivery effectiveness, LNP particle size typically needs to be controlled below 100nm with uniform particle distribution. Microfluidic technology provides a mature solution for this: by dissolving nucleic acids and lipids in separate aqueous and organic phases and rapidly mixing the two phases within a microfluidic chip, lipid nanoparticles are formed in a single step. This not only enables uniform particle size distribution but also allows for precise size control by adjusting the total flow rate and flow rate ratio.
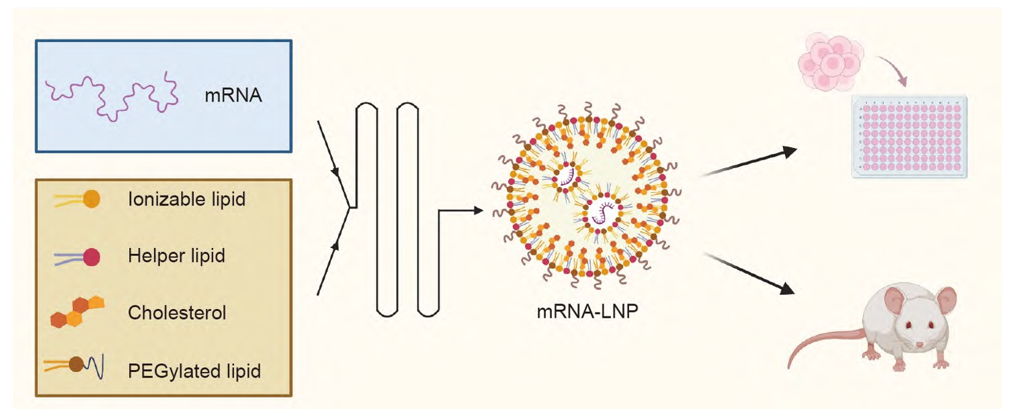
mRNA-LNP Preparation and In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation Diagram
Hydrogel Microspheres
Delivery vectors for small-molecule drugs or growth factors
Hydrogel microspheres can protect, deliver, and locally release drugs (such as small molecule drugs or growth factors). The early use of hydrogel microspheres for drug delivery was in plastic surgery to enable sustained release of growth factors, aiding bone and cartilage repair. Hydrogel microspheres are also frequently used in pulmonary drug delivery and as carriers for growth factor delivery within microtissues. Research has shown that hydrogel microspheres loaded with interleukin-10 can promote cardiac repair, and studies also indicate that hydrogel microspheres can protect insulin from degradation in the stomach, allowing patients to switch from injections to more convenient oral dosing.
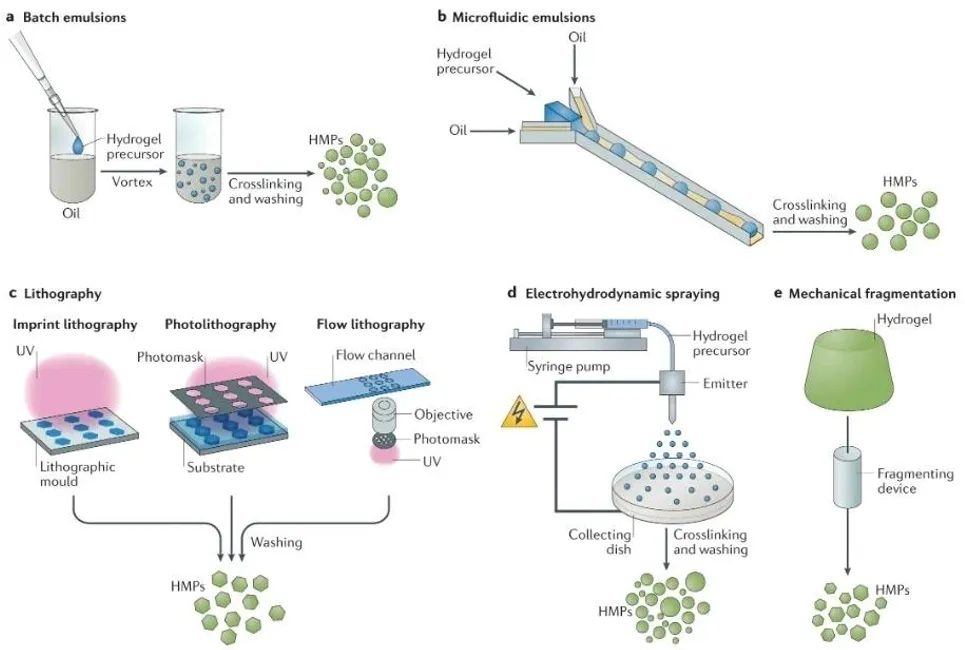
Hydrogel Microsphere Preparation Methods
Common methods for producing hydrogel microspheres include bulk emulsification, microfluidic emulsification, lithography, electrospray, and mechanical fragmentation. The microfluidic emulsification method can effectively control the hydrogel microsphere formation process, yielding microspheres of specified shapes.
Microfluidic Technology Applications in Cosmetics
Functional Skincare Trends
Double-Emulsion Structure
Skincare products with multiple benefits, such as whitening, moisturizing, anti-wrinkle, and anti-aging effects, are highly favored by consumers. This has become a focus of research and marketing for many cosmetics companies. Currently, reliance on a single raw material supplier for popular skincare products has become rare, with improvements in production techniques emerging as key to building a unique brand advantage.
Among skincare products, emulsion-type skincare products (various moisturizers/creams) account for over 70%, and double-emulsion products have even greater application potential. For example, some unstable or oxidized active ingredients like vitamin C and bakuchiol can be fully encapsulated in the inner droplets, with the outer droplets providing protection until the moment of use, allowing absorption by the consumer. This trend is evident in many internationally known products. Furthermore, double emulsions with water/oil/water or oil/water/oil systems enable both oil-soluble and water-soluble ingredients to coexist in a single lotion, supporting formulation design and product efficacy.
Emulsion Technology Comparison
· 1st Generation Mechanical Stirring: Limited in terms of emulsion size distribution and product stability.
· 2nd Generation High-Pressure Homogenization: Good size distribution and stability, but requires more emulsifiers to maintain active ingredient efficacy; achieving multi-layer emulsion structures is challenging.
· 3rd Generation Microfluidic Technology: Under the same formulation, uniform and controlled emulsion size (smaller particle sizes achievable), strong encapsulation of active ingredients, and straightforward multi-layer emulsion design.
Application Cases in Microencapsulated Cosmetics
Several well-known cosmetics companies have already integrated microfluidic technology into their product development and manufacturing.
· Dior Prestige Rose Micro-Oil — Uses microfluidic technology to encapsulate rose extract for maintaining fresh activity, reducing the need for emulsifiers and enhancing formula gentleness.
· Chanel Camellia Repair Cream (Micro-Essence, Cream, Eye Cream)
· Elizabeth Arden Superstart Water Essence + Flawless Start Primer Serum (Hyaluronic Acid)
Microfluidic Technology in Biopesticides
Nanopesticide carrier systems effectively address issues with traditional pesticides, such as low utilization, poor bioavailability, and instability. Professor Zhu Weiping and Yang Yangyang of East China University of Science and Technology’s School of Pharmacy proposed a microfluidic-based nanoparticle platform for continuous production of uniform, efficient lipid nanoparticle-encapsulated dsRNA nano-insecticides, effectively controlling pests like the beet armyworm. LNP encapsulation protects dsRNA from nuclease degradation, enhancing dsRNA stability and cellular delivery, thereby improving RNAi efficacy. This microfluidic nanoparticle platform provides a new pathway for high-quality continuous production of RNAi nanobiopesticides, facilitating the growth of the nanobiopesticide industry.
Morimatsu Intelligent Microfluidic Device
Morimatsu Intelligent Microfluidic Device (IMD-L) serves as a stable, efficient nano-drug preparation platform, providing solutions for laboratory formulation screening and optimization, supporting flow rates from 0.01ml/min to 100ml/min, and synthesis volumes from 1ml to 50ml. It features multiple convenient functions, reducing manual error and experimental burden. When heating is required, Morimatsu's independent temperature control device can be used, with a temperature range of 30°C-65°C within the syringe.

Formula Call
Formula types include cleaning formulas, preparation formulas, and waste discharge formulas. Users can save and call commonly used formulas to easily initiate experiments.
Online Cleaning
Calling the cleaning formula, automatically replenishes cleaning fluid, and completes cleaning tasks, with Sensong providing guidance on the cleaning process.
Automatic Sample Collection
Flexible settings allow for pre- and post-sample waste disposal, enabling unattended batch sample collection, with sample volume set by time or volume.
Operation Status
Real-time display of operation status, with syringe remaining volume, progress, time, and volume clearly visible.
Data Recording
Records operation data in real-time, with exportable data formats supported in Excel for convenient data analysis.
Application Examples
For mRNA-LNP preparation on the IMD-L platform, a flow rate ratio of 1:3 is used for lipid solution and eGFP mRNA solution. The resulting mRNA-LNP solution is filtered with 0.22-micron filtration to yield the final mRNA-LNP product.
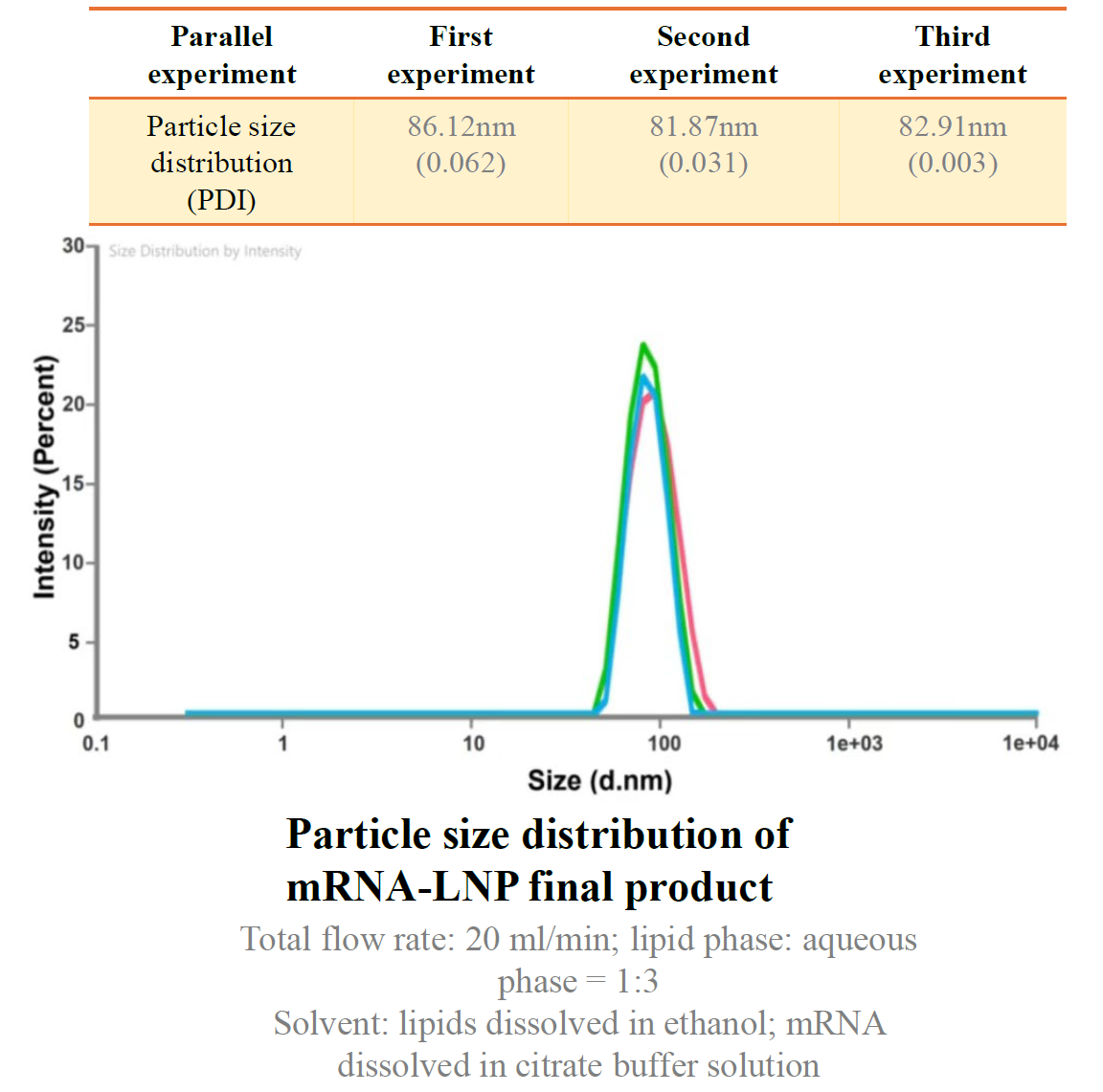
IMD-L demonstrates excellent performance in nanoparticle preparation, with an average particle size of 81-86nm and a PDI of <0.1 across three parallel experiments, achieving uniform particle size and batch stability. The unique lipid formula achieves an encapsulation rate of over 95%, and after 1 month of cold storage, the particle size distribution remains stable.
Morimatsu continues to explore and expand innovative applications of microfluidic technology, providing comprehensive, targeted solutions based on customer needs, supporting research and production advancement.
References
Ji Hongbing, Huang Liyun. "Research Progress on the Application of Microfluidic Technology in the Synthesis of Nano-Microcapsules." Journal of South China Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2018, 50(5):10. DOI: CNKI:SUN.0.2018-05-004.
Jin Yi, Su Mingzhu, Guo Jing, et al. "Preparation of Liposomes by Microfluidic Hydrodynamic Focusing Technology and New Strategies for Targeting Breast Cancer." Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Industry, 2022, 53(06):801-810.
He Tianxi, Liang Qionglin, Wang Jiu, et al. "Microfluidic Preparation of Liposomal Drug Carriers." Progress in Chemistry, 2018, 30(11):1734-1748.
Zong Yan, Wei Tuo, Cheng Qiang. "Development Strategy of Tissue-Specific mRNA-LNP Delivery Technology." Science Bulletin, 2023, 1-10.
[5] Huang X, Ma Y, Ma G,Xia Y. Unlocking the Therapeutic Applicability of LNP-mRNA: Chemistry, Formulation, and Clinical Strategies[J].Research 2024(7): 2639-5274.
[6]Daly AC, Riley L, Segura T,et al. Hydrogel microparticles for biomedical applications[J]. Nat Rev Mater, 2020(05):20–43.
"Aether International: Mass Production of Emulsion and Serum Cosmetics Using Microfluidic Technology."
[8] "MEMS Pioneer: Application of Microfluidic Chips in the Cosmetics Industry."
[9]Jinshan X, Jiaxin Z, Jingyi Y, et al. Microfluidic-Based dsRNA Delivery Nanoplatform for Efficient Spodoptera exigua Control[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2024,72(22):12508-12515.
About Morimatsu LifeSciences
Morimatsu LifeSciences, one of the key business segments of Morimatsu International Holding Co., Ltd. (Morimatsu International, stock code: 2155.HK), mainly consists of Shanghai Morimatsu Pharmaceutical Equipment Engineering Co., Ltd., Morimatsu (Suzhou) Life Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Morimatsu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Pharmadule Morimatsu AB (Sweden) and its subsidiaries, which serves the pharmaceuticals, bio-pharmaceutical, cosmetic medicine, FMCG (cosmetics, baby, women & home Care, health care, fabric & home care, food, beverage, nutraceuticals) and other industries, providing customers with "core equipment+value-added services+digital intelligent overall factory solutions and services" ("MVP Solutions&Services"), focusing on core equipment, stainless steel process systems, disposable process systems, consumables, laboratory solutions, digital and modular factory solutions and services.
As a diversified multinational company, Morimatsu has opened subsidiaries or advanced manufacture plants in China, Japan, Sweden, United States, India, Italy, Singapore, and has delivered different forms of products and services to more than 40 countries and regions so far, by its global footprint of an efficient and professional team.
Forward-Looking Statements
The information in this press release may include some forward-looking statements. Such statements are essentially susceptible to considerable risks and uncertainties. The use of "predicted", "believed", "forecast", "planned" and/or other similar words/phrases in all statements related to our company is to indicate that the statements are forward-looking ones. Our Company undertakes no obligation to constantly revise such predicted statements.
Forward-looking statements are based on our Company management's current perspectives, assumptions, expectations, estimations, predictions and understanding of future affairs at the time of the making of such statements. Such statements are not guarantees of future development and are susceptible to the impact of risks, uncertainties and other factors; some are beyond the control of our Company and unpredictable. Subject to the influence of future changes and development in our business, competition environment, political, economic, legal and social conditions, the actual outcomes may differ significantly from the information contained in the forward-looking statements.