
All cells, whether prokaryotic or eukaryotic, release extracellular vesicles (EVs) during normal physiological activities and pathological changes. These EVs are mainly classified into two categories: ectosomes and exosomes.
Exosomes are nano-sized lipid structures with a diameter ranging from 30 to 150 nm, originating from the invagination of the endoplasmic reticulum to form multivesicular bodies (MVBs). These MVBs can interact with other intracellular vesicles and organelles, increasing the diversity of exosome components.
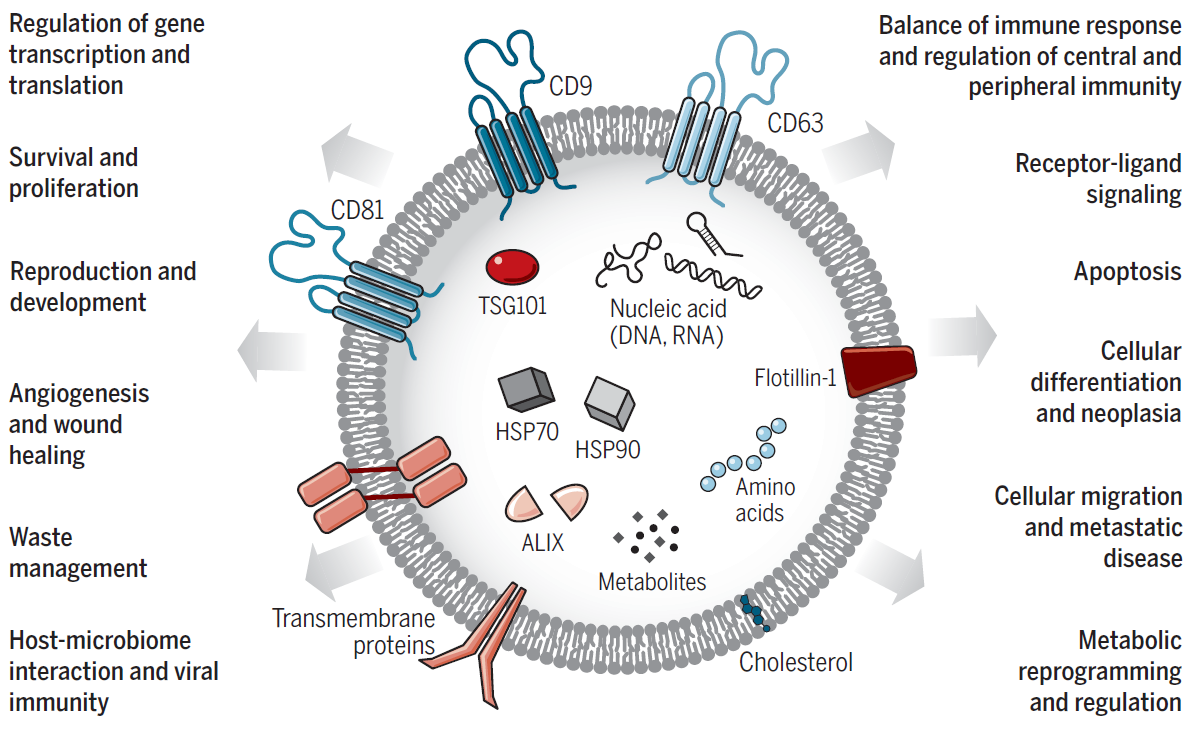
Characteristics of Exosomes
As a pleiotropic intercellular transport system in the human body, exosomes carry a variety of biomolecules such as DNA, RNA, proteins, and lipids, playing a crucial role in the transfer of substances and information between cells.
Application Value of Exosomes
Disease Diagnosis
Exosomes are present in all biological fluids. Through liquid biopsy technology, that is, the analysis of biological fluid samples, exosomes can be obtained and their complex composition can be analyzed for longitudinal sampling to monitor the progression of diseases. The biogenesis of exosomes can capture complex extracellular and intracellular molecules, making them useful for comprehensive multi-parameter diagnostic testing. In addition, the surface proteins of exosomes also contribute to their immunocapture and enrichment. Currently, the key diseases for exosome-based diagnostic applications include cardiovascular diseases, liver diseases, kidney diseases, lung diseases, neurological diseases, and cancers.
Disease Treatment
Exosomes are associated with immune responses, viral pathogenicity, pregnancy, cardiovascular diseases, central nervous system-related diseases, and cancer progression. They can deliver biomolecules such as proteins, metabolites, and nucleic acids to recipient cells, effectively altering their biological responses.
The inherent properties of exosomes in regulating complex intracellular pathways allow for their potential use in the treatment and control of many diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases and cancers. Exosomes can be designed to carry different therapeutic payloads, such as short-interfering RNA, antisense oligonucleotides, chemotherapeutic agents, and immunomodulators, and can precisely deliver these payloads to the target location. The lipid and protein composition of exosomes can affect their pharmacokinetic properties, and their natural components can improve bioavailability and reduce adverse reactions.
Morimatsu's Exosome Manufacturing Process Solutions

Upstream Culture Solutions for Exosomes
Mocellular® 2D WAVE Bioreactor
The Morimatsu 2D Single-Use WAVE Bioreactor provides such advantages such as meeting GMP production requirements, low fixed equipment investment, and no need for cleaning validation at changeover between batches. Combined with its unique two-dimensional rocking mode (as shown in the figure), it offers gas mass transfer capabilities comparable to traditional stirred tank bioreactors. At the same rotational speed, it generates lower fluid shear stress, creating a gentler growing environment ideal for stem cells (iPSC, MSC) and immune cells.

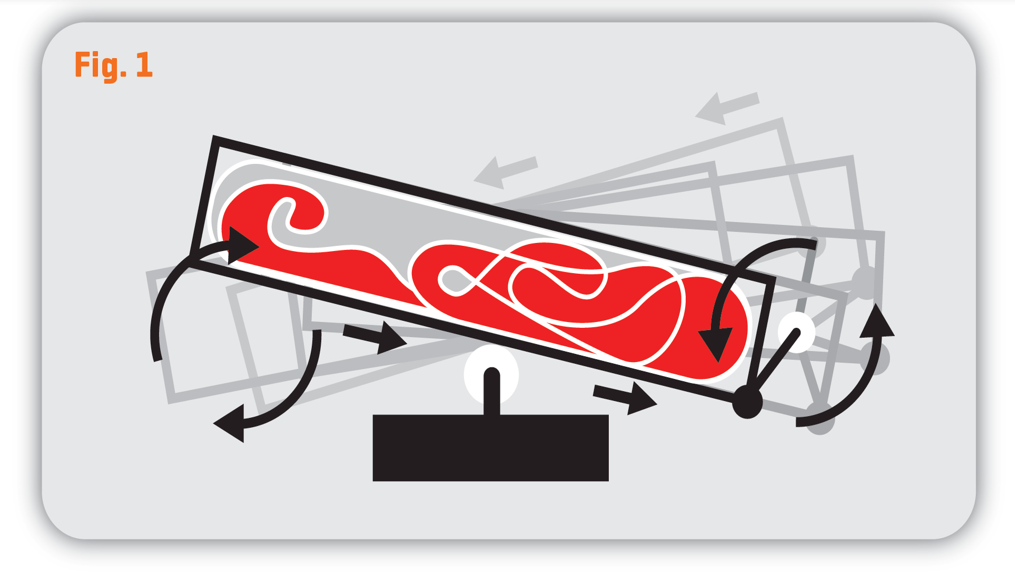
2D WAVE Bioreactor and Its Working Mode
It is experimentally demonstrated that the 2D WAVE Bioreactor performs well in the process of exosome production from MSC cell culture:
It is capable of maintaining the same or even higher cell viability than the stirred tank bioreactor at maximum cell growth density in the same volume.
The final number of exosome particles can reach 1×10^10 or more.
The equipment uses single-use and disposable technology, eliminating the need for cleaning validation between batch changeover during the production process and avoiding cross-contamination.
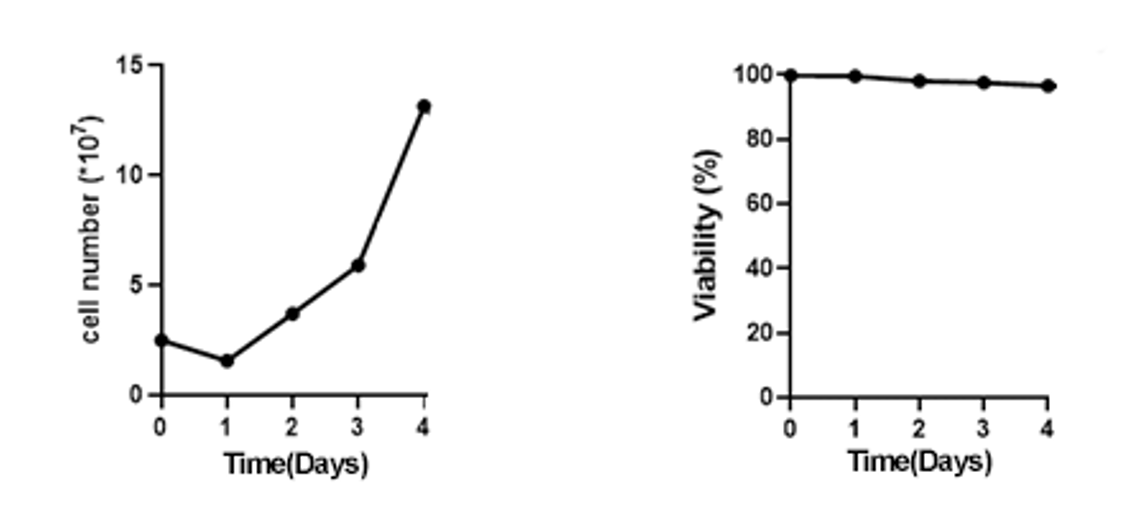
MSC Cell Growth Data
Downstream Purification Solutions for Exosomes
The commonly used exosome separation methods mainly include the following types: ultracentrifugation, immunomagnetic bead method, polyethylene glycol precipitation method (PEG precipitation method), ultrafiltration method, and size-exclusion chromatography (SEC).
| Exosomes Purification Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Ultracentrifugation (Differential Centrifugation) | Reduces contamination and cost associated with separation reagents | 1.High equipment cost, time-consuming, and low production efficiency 2.Damages exosomes, affecting subsequent purification processes, and potential protein |
| Immunomagnetic Bead Method | 1.Separation of exosomes from specific sub-populations 2.Higher purity compared to other methods | 1. High reagent cost and requires pre-identification of exosome tag proteins 2.Low sample processing capacity and only tagged exosomes can be recognized |
| PEG Precipitation Method | 1.Easy to operate, no special instruments required 2. High sample processing capacity and scalable | 1.Lack of selectivity and easy to co-precipitate with exosome contaminants 2.Long purification time, requires pre-removal of lipoprotein and other subcellular particles, and remove polymer materials after separation |
| Ultrafiltration Method | Fast purification speed, simple and mature process | 1.Medium purity 2.Shear force may cause exosome damage, leading to aggregation and vesicle entrapment in membrane pores or loss of exosomes adsorbed on the membrane |
| Size - Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) | 1.High-purity exosomes 2.Preserves the integrity and bioactivity of exosomes 3. Good reproducibility | 1.Medium-high instrument cost 2.Long purification operation time |
Based on the requirements for exosome harvest purity, batch-to-batch stability, operational reproducibility, etc., the ultrafiltration method and size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) are widely accepted in the industry due to their high operational convenience and technological maturity.
MoPurity® Filtration System
The MoPurity®SUF benchtop single-use filtration system can be used for TFF as well as DF/VF/SPTFF processes. With its unique four-in-one functional innovative design, multiple process steps in exosome purification are integrated into one system. It is easy to operate, meets GMP production requirements, saves space and fixed-asset investment, and avoids cross-contamination between batches.

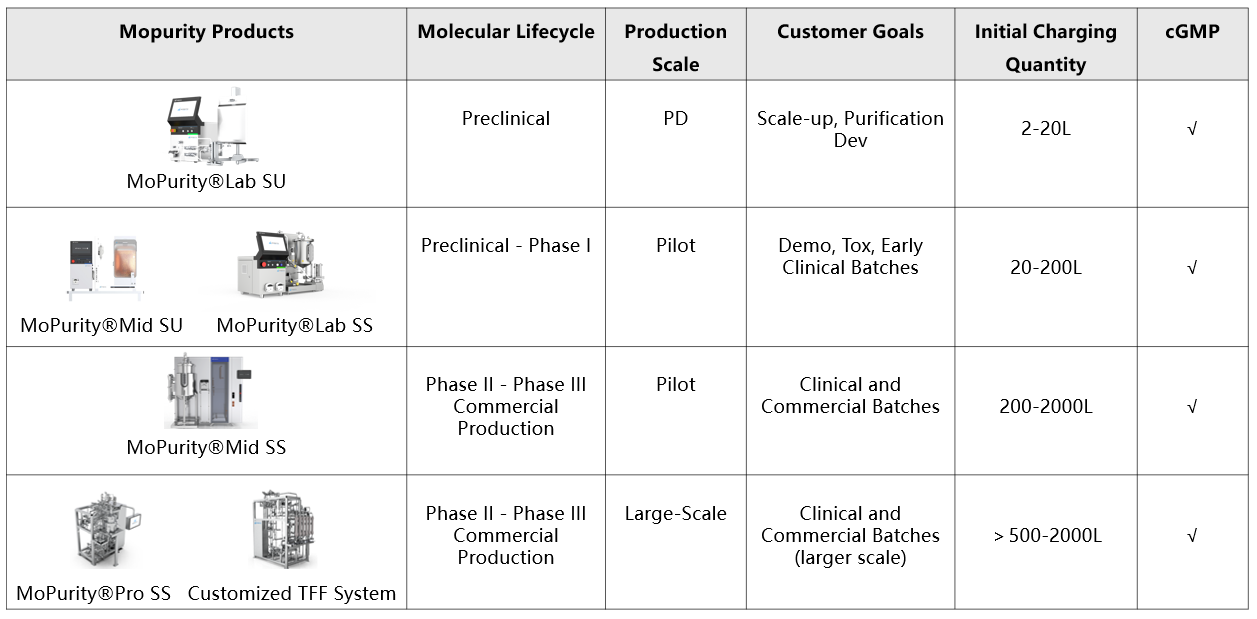
The MoPurity® series of products offers purification solutions for the entire product lifecycle, tailored to the customer's product stage.
MoChroma® Chromatography System
The MoChroma® chromatography system can address different purification challenges. It is mainly used for the rapid purification of target products such as proteins, polypeptides, and nucleic acids, supporting mainstream chromatography techniques such as affinity, ion exchange, hydrophobic interaction, molecular sieve, reverse phase, and multi-mode. Its control software integrates functions such as system control, method editing, data analysis, user permission management, and audit trail to ensure sufficient data security and integrity.


MoTransit® Small-Batch Filling System
The MoTransit® small-batch filling system is a powerful and stable filling system compliant with GMP production requirements. Under Class A laminar flow protection and with the cooperation of robots, it meets the needs of small-batch filling and rapid filling of various packaging formats such as disposable liquid storage bags and vials, facilitating the rapid launch of exosome-based drugs.

Digital and Intelligent Services
The Morimatsu EPCOO integrated solution provides full-lifecycle empowerment services for pharmaceuticals, creating a digital twin of each stage, including design, procurement, construction, operation, and optimization to form a twin star of engineering and software. Thus, it provides digital and intelligent services for exosome production, including material management, equipment operation and maintenance monitoring, data integration and analysis, optimization suggestions, etc., covering the entire pharmaceutical production process.
Due to their unique biological characteristics, exosomes are considered an important breakthrough in the future biomedical field. As research continues and technologies evolve, the application potential of exosomes is even broader. Morimatsu provides a comprehensive solution for the exosome field, helping customers accelerate the development process, meet industrialization needs, and contribute to human health.
About Morimatsu LifeSciences
Morimatsu LifeSciences, one of the key business segments of Morimatsu International Holding Co., Ltd. (Morimatsu International, stock code: 2155.HK), mainly consists of Shanghai Morimatsu Pharmaceutical Equipment Engineering Co., Ltd., Morimatsu (Suzhou) Life Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Morimatsu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Pharmadule Morimatsu AB (Sweden) and its subsidiaries, which serves the pharmaceuticals, bio-pharmaceutical, cosmetic medicine, FMCG (cosmetics, baby, women & home Care, health care, fabric & home care, food, beverage, nutraceuticals) and other industries, providing customers with "core equipment+value-added services+digital intelligent overall factory solutions and services" ("MVP Solutions&Services"), focusing on core equipment, stainless steel process systems, disposable process systems, consumables, laboratory solutions, digital and modular factory solutions and services.
As a diversified multinational company, Morimatsu has opened subsidiaries or advanced manufacture plants in China, Japan, Sweden, United States, India, Italy, Singapore, and has delivered different forms of products and services to more than 40 countries and regions so far, by its global footprint of an efficient and professional team.
Forward-Looking Statements
The information in this press release may include some forward-looking statements. Such statements are essentially susceptible to considerable risks and uncertainties. The use of "predicted", "believed", "forecast", "planned" and/or other similar words/phrases in all statements related to our company is to indicate that the statements are forward-looking ones. Our Company undertakes no obligation to constantly revise such predicted statements.
Forward-looking statements are based on our Company management's current perspectives, assumptions, expectations, estimations, predictions and understanding of future affairs at the time of the making of such statements. Such statements are not guarantees of future development and are susceptible to the impact of risks, uncertainties and other factors; some are beyond the control of our Company and unpredictable. Subject to the influence of future changes and development in our business, competition environment, political, economic, legal and social conditions, the actual outcomes may differ significantly from the information contained in the forward-looking statements.