
Collagen is a high-molecular functional protein. Collagen is the most abundant and widely distributed protein in the mammalian body, making up 25% to 30% of the total protein content in humans. It accounts for as much as 70% of the composition of the skin.

Collagen features a unique triple helix structure, composed of three polypeptide chains intricately intertwined. This distinctive structure imparts collagen with exceptional stability and tensile strength.
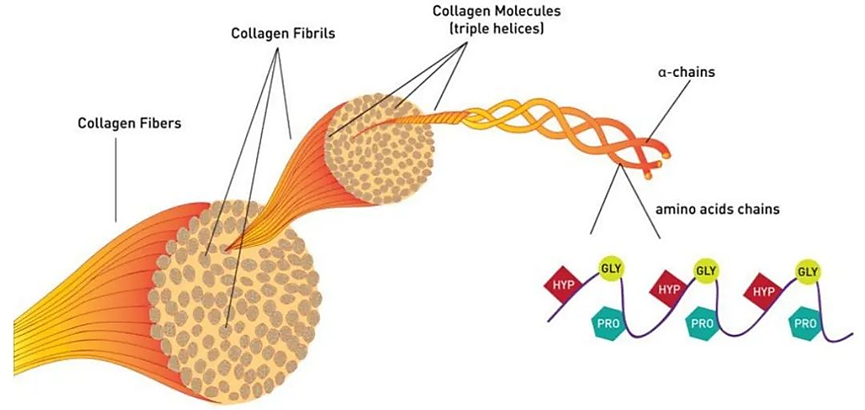
Collagen Structure Diagram
There are at least 28 known types of collagen, each playing a distinct role in the body’s structure and function. For example, Type I is primarily found in the skin, tendons, ligaments, bones, and teeth. It provides exceptional tensile strength and durability. Type II is primarily located in cartilage and joint tissues, contributing to the elasticity of joints and acting as a cushion to reduce impact. Type III is present in the dermis layer of the skin, sclera, blood vessels, and other tissues. It is closely associated with skin elasticity and hydration, playing a crucial role in maintaining skin health and youthfulness.
Application Areas of Collagen
1.Scaffold Material in Tissue Engineering
Collagen is widely used as a scaffold material in tissue engineering. Take heart valve repair materials as an example. Due to its excellent biocompatibility and degradability, it can provide an optimal environment for cell growth. Collagen scaffolds can mimic the natural structure of heart valves, promoting cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. This facilitates the repair and regeneration of damaged heart valves.
2.Food Additives
In meat products, collagen can be used as a modifier that affects the tenderness of the meat and the texture of the muscles after the meat has been cooked. Studies have shown that the higher the collagen content, the firmer the texture of the meat. For example, the tenderness of fish is considered to be related to the degradation of Type V collagen. The cleavage of peripheral cellular collagen fibers caused by the destruction of its peptide bonds is thought to be the main cause of the muscle tenderization phenomenon. By disrupting the hydrogen bonds within collagen molecules, its tightly coiled superhelical structure is broken down, forming gelatin with smaller, looser molecules. This not only enhances meat tenderness but also increases the value and protein content, balancing both taste and nutritional value.
3.Medical Beauty
01.Fillers
Compared to traditional filler materials, collagen fillers offer more durable and natural results. They integrate better with human tissue, avoiding the sensation of foreign bodies that can occur with other fillers. In China, only a few companies are licensed to produce collagen fillers, including Sunmax Biotechnology in Taiwam, Artecoll in Hafod, FILLDERM from Changchun Botai, and WYE-MOR from Jinbo. These products are extracted and purified from specific pathogen-free (SPF) pigs, ensuring high safety by isolating animal viruses from the source.
02.Promoting Collagen Regeneration
Collagen fillers promote collagen regeneration. The undenatured collagen, with telopeptides removed, is antigen-resistant, biocompatible, and biodegradable, which supports the survival and growth of fibroblasts. In addition to filling wrinkles, collagen fillers enhance tissue activity, stimulate skin cell regeneration and repair, and improve skin elasticity and firmness. When compared to hyaluronic acid, collagen fillers are particularly effective for treating tear troughs and dark circles under the eyes. They also have the added benefit of inhibiting melanin production, offering a whitening effect without the risk of the Tyndall effect.
4.Beauty Industry
01.Moisturizing and Whitening
As consumers shift their skincare focus from basic maintenance to targeted efficacy, products with proven results are becoming increasingly popular. Collagen is a key component of the skin. Its high concentration in the skin allows it to form a protective moisturizing film on the surface, which helps prevent water loss and keeps the skin hydrated. Collagen can also inhibit melanin production, accelerate skin metabolism, and reduce pigmentation and dullness, contributing to brighter, fairer skin.
02.Repair and Wound Healing
In terms of skin cosmetology, humanoid collagen is commonly used in products such as eye masks, face masks, and sprays to help repair skin issues like dermatitis, acne, and sensitivity. For example, efficacy tests have shown that Jiaoli's active collagen firming and anti-wrinkle serum, along with its essence mask, promote cell proliferation (specifically CCC-ESF-1 cells), resulting in firming and anti-wrinkle effects.
In the medical field, humanoid collagen is utilized as a wound dressing. It absorbs wound exudates, promotes fibroblast chemotaxis, and accelerates the healing process. With its biological activity, it stimulates the growth and regeneration of epidermal cells, supporting the repair of acne and sensitive skin barriers. Additionally, its film-forming properties help create a protective, moisturizing layer on the skin's surface, replenishing collagen and alleviating skin issues.
Collagen Production Technology
Traditional methods of collagen extraction primarily rely on animal tissues. However, these approaches have several limitations, including resource constraints, the potential for pathogen transmission, and the complexity of the extraction process. The advent of genetic engineering has provided new opportunities for collagen production.
Recombinant collagen involves cloning the human collagen gene into an expression host using genetic engineering techniques. Through processes such as expression and purification, high-purity collagen with stable quality can be obtained.
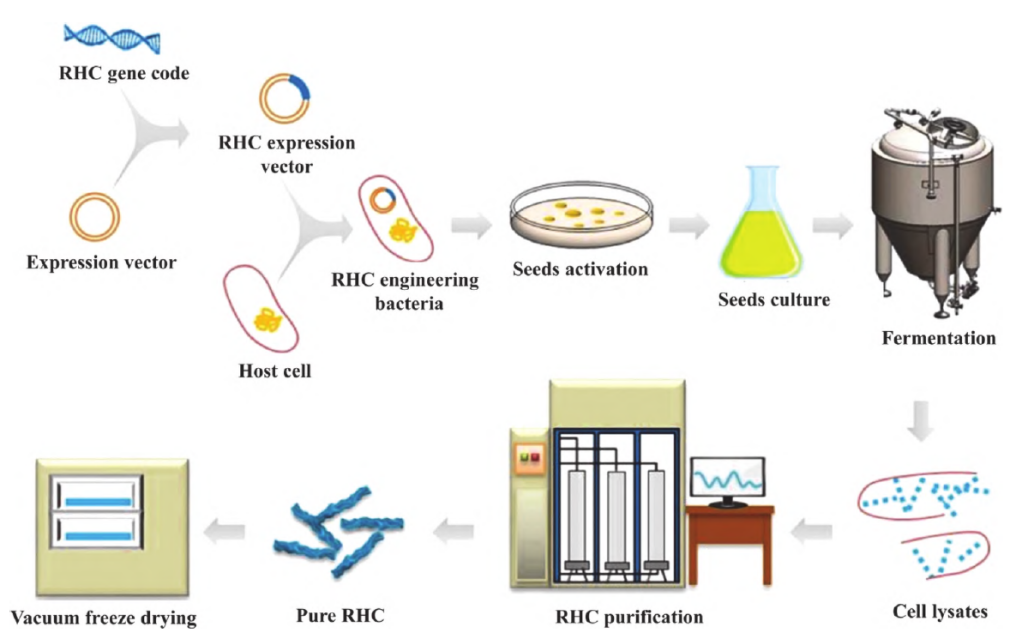
Schematic Diagram of Recombinant Collagen Production Process
Compared to traditional extraction methods, the production of recombinant collagen offers several advantages:
High safety:Recombinant collagen eliminates the risk of disease transmission associated with animal-derived materials, such as contamination by viruses and pathogens.
Batch consistency:The controlled production process ensures high consistency between batches, maintaining uniform product quality.
Single component:The molecular structure of recombinant collagen is homogeneous and easier to control and purify, avoiding the complexity of multiple protein mixtures found in traditional methods.
High activity:Genetic engineering techniques allow for an increase in hydrophilic amino acids, enhancing the collagen’s hydrophilicity. This is particularly beneficial for applications like tissue engineering.
No immune rejection:Recombinant collagen has low immunogenicity, minimizing the risk of immune rejection when used in implanted materials.
Better processability:Recombinant collagen is more water-soluble, improving its processability for various applications.
Increased bioactivity:The recombinant single-chain structure offers more active binding sites. Even when in its triple-helix form, recombinant collagen has a looser structure compared to natural tissue collagen, exposing more biologically active regions. This makes it easier for collagen to interact with cells and bioactive molecules.
Antioxidant properties:Recombinant collagen demonstrates stronger chelation abilities with metal ions such as iron, copper, mercury, and cadmium, providing enhanced antioxidant effects that help reduce oxidative damage to the skin and contribute to whitening effects.
Morimatsu's Solutions in the Field of Genetic Reorganization
In the field of genetic recombination and biological engineering, Morimatsu offers a comprehensive range of production biofermenters, including 1KL, 2KL, 3KL, 5KL, 10KL, 20KL, 30KL, and 100KL models. Alongside these, the company provides essential systems and equipment such as seed tanks, replenishment systems, media preparation systems, and downstream separation and purification systems. With extensive experience in design, manufacturing, commissioning, and testing, Morimatsu is particularly skilled in the scale-up design of high-density fermentation processes.
Recently, Morimatsu has supplied 5KL, 10KL, and 20KL biofermenters, along with supporting systems, to customers in the field of genetically recombinant collagen production. These systems utilize E. coli and Picrosporum as expression vectors for collagen synthesis.
To meet domestic and international validation standards, Morimatsu has leveraged its expertise in high-density fermentation, adopting advanced amplification design theory and calculation methods. Using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) flow field simulations and an extensive database, the company has conducted detailed design and validation of various key components, including the fermenter’s height-to-diameter ratio, the design and number of stirring and baffling elements, the configuration of the vent pipe openings, and the form of the inner and outer jackets. These design enhancements enable the high-density fermenter to achieve the necessary oxygen transfer rate (OTR), volumetric mass transfer coefficient (KLa), cooling capacity, and heat transfer area.
The fermenter is equipped with a clean interior and features a customized automatic cleaning system on the exterior. This ensures efficient cleaning while conserving water and electricity.
Recombinant collagen holds significant potential in the medical beauty market, offering promising prospects for various applications. Morimatsu is committed to helping customers achieve technological breakthroughs, build core competitive advantages, and contribute to the high-quality development of the medical beauty industry. This work not only meets the growing demand for medical beauty solutions but also ignites a new engine for health and beauty.
About Morimatsu LifeSciences
Morimatsu LifeSciences, one of the key business segments of Morimatsu International Holding Co., Ltd. (Morimatsu International, stock code: 2155.HK), mainly consists of Shanghai Morimatsu Pharmaceutical Equipment Engineering Co., Ltd., Morimatsu (Suzhou) Life Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Morimatsu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Pharmadule Morimatsu AB (Sweden) and its subsidiaries, which serves the pharmaceuticals, bio-pharmaceutical, cosmetic medicine, FMCG (cosmetics, baby, women & home Care, health care, fabric & home care, food, beverage, nutraceuticals) and other industries, providing customers with "core equipment+value-added services+digital intelligent overall factory solutions and services" ("MVP Solutions&Services"), focusing on core equipment, stainless steel process systems, disposable process systems, consumables, laboratory solutions, digital and modular factory solutions and services.
As a diversified multinational company, Morimatsu has opened subsidiaries or advanced manufacture plants in China, Japan, Sweden, United States, India, Italy, Singapore, and has delivered different forms of products and services to more than 40 countries and regions so far, by its global footprint of an efficient and professional team.
Forward-Looking Statements
The information in this press release may include some forward-looking statements. Such statements are essentially susceptible to considerable risks and uncertainties. The use of "predicted", "believed", "forecast", "planned" and/or other similar words/phrases in all statements related to our company is to indicate that the statements are forward-looking ones. Our Company undertakes no obligation to constantly revise such predicted statements.
Forward-looking statements are based on our Company management's current perspectives, assumptions, expectations, estimations, predictions and understanding of future affairs at the time of the making of such statements. Such statements are not guarantees of future development and are susceptible to the impact of risks, uncertainties and other factors; some are beyond the control of our Company and unpredictable. Subject to the influence of future changes and development in our business, competition environment, political, economic, legal and social conditions, the actual outcomes may differ significantly from the information contained in the forward-looking statements.